|
Cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum Maton.)
Zingiberaceae
Cardamom, popularly known as Queen of Spices is native to the evergreen rainy forests of Western Ghats in South India. It is cultivated in about 1, 00,000 ha mainly confined to the Southern States viz; Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu accounting for 60,31 and 9% of the total area respectively. Our annual production is about 40000 metric tonnes and nearly 40% of which is exported to more than 60 countries earning a foreign exchange of nearly 60 million rupees. Cardamom is used for flavouring various preparations of food, confectionary, beverages and liquors.
Varieties
Malabar : Mudigree 1, Mudigree 2, PV 1, PV-3, ICRI 1, ICRI 3, TKD 4,IISR Suvarna, IISR Vijetha, IISR Avinash, TDK - 11 ,
CCS-1 ,
Suvasini ,
Avinash ,
Vijetha - 1 ,
Appangala 2,Njallani (Green gold),
ICRI 8
Mysore
ICRI 2 ,
Vazhukka
MCC -12 ,
MCC -16 ,
MCC -40 ,
PV2, PV5
.
 |
 |
 |
Cardamom Plantation |
Cardamom Plant |
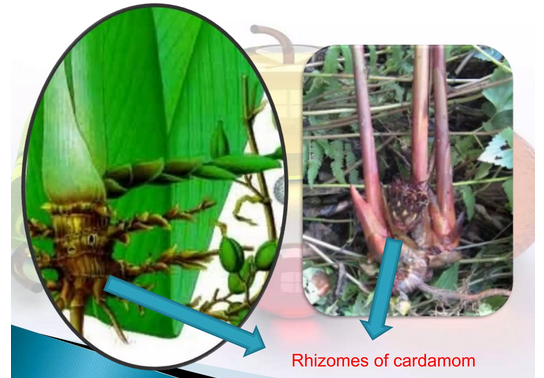
Rhizomes of cardamom |
Soil and climate
Thick shady areas with loamy soil are ideal for cultivating cardamom. This crop can be grown at an elevation from 600 to 1500 m. Areas exposed to heavy winds are unsuitable. Adequate drainage must be provided. It is grown in forest loamy soils which are usually acidic in nature with a pH range of 5.0 – 6.5
Season
June – December is found to be optimum.
Seeds and sowing
Seedlings/suckers can be used for propagation.
Propagation from Seeds
-
Collect seeds from healthy and high yielding plants.
-
Seed rate – 600g/ha (fresh seeds).
-
Treat with commercial grade Sulphuric acid or Hydrochloric acid for 20 minutes.
-
Wash with water.
-
Prepare the beds with equal quantity of well rotten cattle manure, wood ash and jungle soil.
-
Sow the seeds in beds and cover with a thin layer of fine sand.
 |
Cardamom seedling raising |
-
Mulching and shading may be provided to seed beds. The beds should be kept moist but not too wet. Germination starts usually a month after sowing and continues upto three months. seedlings are transplanted to secondary nursery at 3 to 4 leaf stage.
Secondary nursery:
-
Prepare the beds. As that of primary nursery, shade is provided by erecting overhead pandal.
-
Seedlings planted at a distance of 20 x 20 cm.
-
Polybags of 20 x 20 cm size can be used.
 |
Cardamom secondary nursery |
Propagation from suckers:
The suckers are commonly used for gap filling but suckers may not be available in larger numbers. Therefore, a rapid Clonal multiplication technique evolved by Indian Institute of Spice Research, Cardamom Research Centre, Appangala, is proved to be quick, reliable and economic for production of large number of quality planting materials. The site selected for this method should have a gentle slope and have a water source nearby it. Trenches of 45cm width, 45 cm depth and of any convenient length may be taken across the slope or along the contour at 1.8 m apart. The top 20 cm depth soil is excavated separately and heaped on the upper side of the trench. The lower 25 cm is excavated and heaped on the lower side of the trenches all along the line. The top soil is mixed with equal portions of top soil is mixed with equal proportions of humus rich jungle soil, sand and cattle manure and filled back by leaving a depression of 5 cm at the top to facilitate mulching for retention of soil mixture. Suckers, each consisting of one grown up tiller and a growing young shoot, are placed at a distance of 0.6 m distance in the trenches during March-October. Regular cultural operations are to be followed including high fertilizer dosed 100:50:200 kg NPK/ha in 6 split doses at 60 days interval along with Neem cake at 250 g/plant. Irrigation should be provided atleast twice in a week. Overhead pandal at a height of 3.6 m covered with coir mat or leafy twigs of any shade tree may be provided during the non-rainy season. Within a period of 12 months, a plant would produce atleast 32 to 42 suckers, which may yield at least 16 to 21 planting units per ha of clonal nursery within 12 months of planting.
 |
| Rapid clonal multiplication |
Preparation of the field
Dig pits of 60 cm x 60 cm x 60 cm size and fill with compost and top soil. Contour planting may be done in slopy areas.18-22 months old seedlings are used for transplanting.
Spacing
Larger types : 2.5 x 2.0 m.
Smaller types : 2.0 x 1.5 m.
Irrigation
Generally Cardamom is grown as a rainfed crop, but provide sprinkler irrigation during summer for increased yields.
Manuring
Apply compost 25 t/ha; 75 kg N; 75 kg P and 150 kg K/ha in two split doses during June ‑ July and October - November.
After cultivation
-
Shade regulation : Moderate shade : 50-60 %, Rainfed : 40 – 50 %, Irrigated : 55-60 %
-
Mixed population of medium sized shade trees - karuna , Red cedar, konikonna, Jack, Vellakil, Thempavu, Thambahom, Bolongi, Elangi.
-
Weed the field as and when necessary. Towards the end of monsoon rains, a light raking or digging and mulching is given around the plant to a radius of about 75 cm to conserve moisture during the dry period.
-
Pollination can be enhanced by keeping bee hives at 10 – 15 Nos./ha.
Plant protection
Pests
Thrips
| Pesticide |
Dose |
| Diafenthiuron |
50 % WP 8 g/10 lit |
| Monocrotophos |
36 % SL 10 ml/10 lit |
| Phenthoate |
50 % EC 5.0 ml/10 lit. |
| Quinalphos |
25 % EC 12 ml/10 lit. |
Hairy caterpillar
Hairy caterpillar can be controlled by spraying Phosalone 35 EC 1 ml/lit.
Shoot and fruit borer
Setup pheromone trap @ 12 Nos/ha to attract and destroy the female moths.
Mites
Mites can be controlled by spraying Dicofol 18.5 EC 2 ml/lit.
Nematode
Fumigate the primary and secondary nursery beds using Methyl Bromide (@ 500 g/10 sq.m) or Ethylene-di-bromide (@ 20 lit/ha) or Durofume (@ 30 lit/ha) under polythene cover for 2-3 days or drench the nursery beds with 2 % Formalin.
Apply Carbofuran 3 G @ 5 kg a.i/ha
Diseases
Mosaic or Katte disease
This is a serious disease affecting the productivity of Cardamom.
This is transmitted by banana aphid which can be controlled by regular spraying with Methyl demeton 25 EC or Dimethoate 30 EC or Phosphomidon 86 WSC at 750 ml/ha.
Damping off or clump rot or rhizome rot
Drench nursery with 1 lit of Formaldehyde in 50 lit water for 3 sq.m. before sowing. Prophylactic drench with 0.25% Mancozeb or 1% Bordeaux mixture immediately after germination to control Pythium and 0.05% Carbendazim after 15 days to control Rhizoctonia.
Capsule rot or panicle rot or Azhukal
Three sprays with 1% Bordeaux mixture or 0.25% Copper oxychloride or 0.2% Mancozeb just before onset of South West monsoon in early August and in September. Drench the soil with 1% Bordeaux mixture.
 |
 |
Cardamom Flower |
Cardamom Immature Capsules |
Harvesting and Processing
Cardamom plants normally start bearing two years after planting. In most of the areas the peak period of harvest is during October- November. Picking is carried out at an interval of 15-25 days. Ripe capsules are harvested in order to get maximum green colour during curing.
After harvest, capsules are dried either in fuel kiln or in electrical drier or in the sun. It has been found that soaking the freshly harvested green cardamom capsules in 2%washing soda for 10 minutes prior to drying helps to retain the green colour during drying. When drier is used, it should be dried at 45 to 500C for 14 to 18 hours, while for kiln, over night drying at 50 to 600C is required. The capsule kept for drying are spread thinly and stirred frequently to ensure uniform drying. The dried capsules are rubbed with hands or coir mat or wire mesh and winnowed to remove any foreign matter. They are then sorted out according to size and colour, and stored in black polythene bag to retain the green colour during storage. These bags are then kept in wooden chambers.
 |
 |
Cardamom Capsules |
Cardamom Seeds |
Yield
The yield ranges from 200 - 250 kg/ha.
Market information
| Growing districts |
Theni |
| Major markets in Tamil Nadu |
Bodinayakanur, Kumily, Thekkady, Kumbum |
| Preferred varieties |
Alleppey Green Extra Bold' (AGEB) |
| Grade specification |
Freshness, colour, aroma and size |
|










